HIV Statistics
Syndemic Data
Syphilis
Annual syphilis screening increased from 5.7% in 2022 to 16.3% in 2024. (source: IHS Clinical Reporting System)
HCV
Since IHS initiated hepatitis C virus (HCV) screening of the birth cohort of “baby boomers” (persons born 1945-1965), HCV screening has increased from 8% to 73% of the IHS user population. Screening of all persons over 18 years of age for HCV has reached 58%. (source: Clinical Reporting System)
HIV
- Since the 2006 recommendation to screen all persons for HIV, IHS has screened 60% of its adolescent and adult patients. (source: IHS Clinical Reporting System)
- Between 2019 and 2024, 35% of all adolescent and adult active patients in the IHS system have been tested for HIV. (source: IHS Clinical Reporting System)
- From 2016 to 2022, new diagnoses in the IHS Areas with the highest HIV burden have dropped by 23%. (source: IHS National Data Warehouse/Division of Epidemiology and Disease Prevention with CDC collaboration)
- The largest HIV ART programs in IHS achieved 90% viral suppression among its patients with HIV in 2024. (source: annual facility reports from ART programs)
HIV DATA
View the latest data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) on HIV by race and ethnicity.
HIV is a public health issue among American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) people, who represent about 1.7% of the U.S. population. Compared with other racial/ethnic groups, AI/AN ranked fifth in the rate of new HIV diagnoses in 2022*, with lower rates than Blacks/African Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, Native Hawaiians/Other Pacific Islanders, and people reporting multiple races, but higher rates than among Asians and Whites.
Key Statistics about HIV Among American Indian/Alaska Native People
- In 2022, there were 215 new diagnoses of HIV infection among AI/AN people.
- The number of new diagnoses in 2022 represents an increase of 4 new diagnoses from 211 in 2021 but an increase of 49 new diagnoses from 166 in 2018.
- Males accounted for 73.5% (158) of all new diagnoses, a decrease from 78.2% of all new HIV diagnoses in 2021 and a decrease from 82% in 2018.
- Women accounted for 26.5% (57) of all new diagnoses, an increase of 11 cases from 46 in 2021 and from 30 diagnoses in 2018.
- 25-34-year-olds (85 new diagnoses) and 35-44-year-olds (58 new diagnoses) together accounted for 66.5% of all new HIV diagnoses among AI/AN.
- The primary mode of transmission among men is male-to-male sexual contact (114 new diagnoses out of 158 total diagnoses for men);
- Among women, the primary mode of transmission is heterosexual contact (31 out of a total of 57 new diagnoses among women)
- In 2022, out of every 100 AI/AN people with diagnosed HIV, 76 persons received some care, 54 persons were retained in care, and 65 persons had achieved viral suppression – in line with the national average (graphic)1.
Disparities in HIV Experienced by American Indian/Alaska Native People
- In 2022, the rate of new HIV diagnoses among AI/AN people was 10.6 (per 100,000 population), twice the rate of 5.3 (per 100,000 population) experienced by Whites.
- Between 2018 and 2022, new HIV diagnoses among AI/AN people increased by 30%, from 166 new HIV diagnoses in 2018 to 215 new HIV diagnoses in 2022.
- In 2022, AI/AN people had the lowest level of knowledge of HIV status (77.3%) than any other racial or ethnic group.
- In 2022, the rate of diagnosis of HIV infection among AI/AN women, 5.5 per 100,000 population, was over twice as high as the rate of diagnosis among White women (1.9%).
- In 2022, AI/AN women diagnosed with HIV had the second highest percentage (46%) of HIV infections attributable to injection drug use when compared to women in other racial or ethnic groups.
HIV Diagnoses Among American Indian/Alaska Native People by Transmission Category and Sex, 2022 – United States
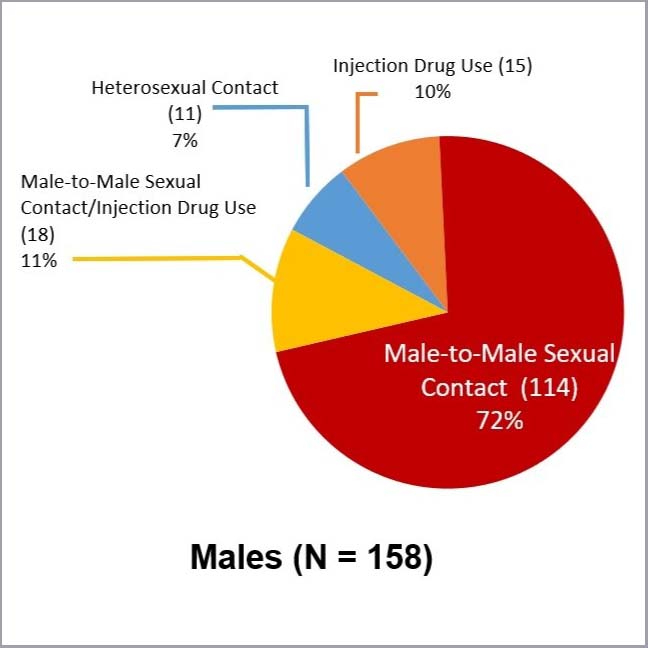
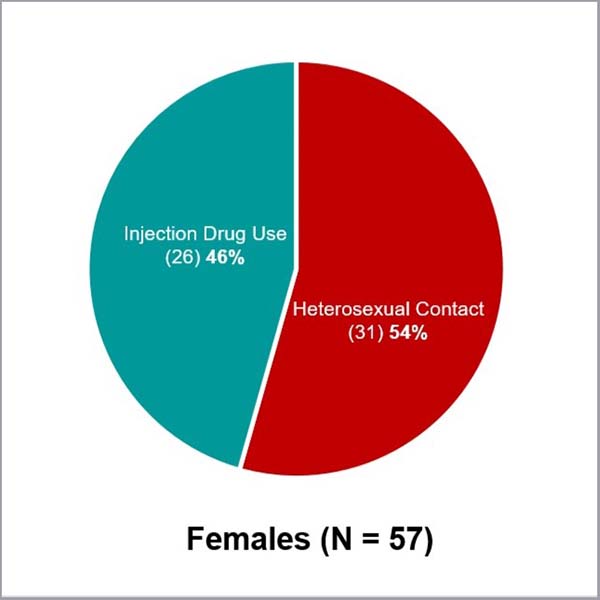
The terms male-to-male sexual contact (MSM) and male-to-male sexual contact and injection drug use (MSM/IDU) are used in CDC surveillance systems. They indicate the behaviors that transmit HIV infection, not how individuals self-identify in terms of their sexuality.
ADDITIONAL DATA RESOURCES
AtlasPlus – an interactive tool from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that gives users the ability to create customized tables, maps, and charts using nearly 20 years of CDC’s surveillance data on HIV, viral hepatitis, STD, and TB. AtlasPlus also provides access to indicators on social determinants of health (SDOH) allowing users to view social and economic data in conjunction with surveillance data for each disease.
America’s HIV Epidemic Analysis Dashboard (AHEAD) – an interactive tool developed by the HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health that displays national progress toward meeting the goals of the Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. (EHE) initiative. Users can filter CDC data by race/ethnicity, age, sex, and mode of HIV transmission for the six EHE indicators.
Ryan White HIV/AIDS Program (RWHAP) Compass Dashboard – an interactive tool developed by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) that allows users to visualize the reach, impact, and outcomes of the RWHAP. The dashboard provides a look at national-, state-, and metro area-level data and allows users to explore RWHAP client characteristics and outcomes, including age, housing status, transmission category, and viral suppression. The RWHAP Compass Dashboard also visualizes information about RWHAP services received and characteristics of those clients accessing the AIDS Drug Assistance Program (ADAP).
HIV by Race and Ethnicity – While HIV affects all races and ethnicities in the United States and dependent areas, some groups are disproportionately affected compared to their population size. Get the latest data from CDC on HIV by race and ethnicity.
*Unless otherwise noted, all statistics are based on calculations made using data from CDC's AtlasPlus. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. NCHHSTP AtlasPlus. Accessed May 28, 2024.
1 Source: CDC. HIV Surveillance Supplemental Report: Monitoring Select National HIV Prevention and Care Objectives by Using HIV Surveillance Data—United States and 6 Freely Associated States, 2022. Published Date: 05/21/2024


